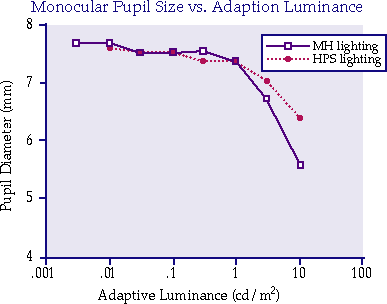
Applying Research on Night VisionPerception of Color, Brightness, and ClarityPurposeWe compared visual performance under high pressure sodium (HPS) and metal halide (MH) lamps to extend the LRC's basic research on nighttime (mesopic) visual function into the areas of perception of color, brightness, and clarity. This study indicates that MH lamps are superior to HPS lamps for nighttime applications where off-axis visual tasks are performed. Reaction Time: At three typical nighttime luminances (1 cd/m 2, 0.1 cd/m 2 and 0.01 cd/m 2), reaction times to small, flashed, off-axis targets were significantly less under MH lamps than under HPS lamps for equal luminances. This difference was greatest at the lowest mesopic levels. Reaction times to on-axis targets were equal for both sources at equal luminances. Sponsor: U.S. Army |
Advancing the effective use of light for society and the environment